Chandrayaan-3
A. Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 is India's third lunar exploration mission planned by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The mission is a follow-up to Chandrayaan-2, which aimed to explore the moon's south polar region but faced challenges with its lander, Vikram. Chandrayaan-3 is designed to build upon the success of Chandrayaan-2 and further India's exploration of the lunar surface.
B.Chandrayaan-3 Objectives
Chandrayaan-3, India's third lunar exploration mission, aims to achieve the following objectives:
Primary Objectives:
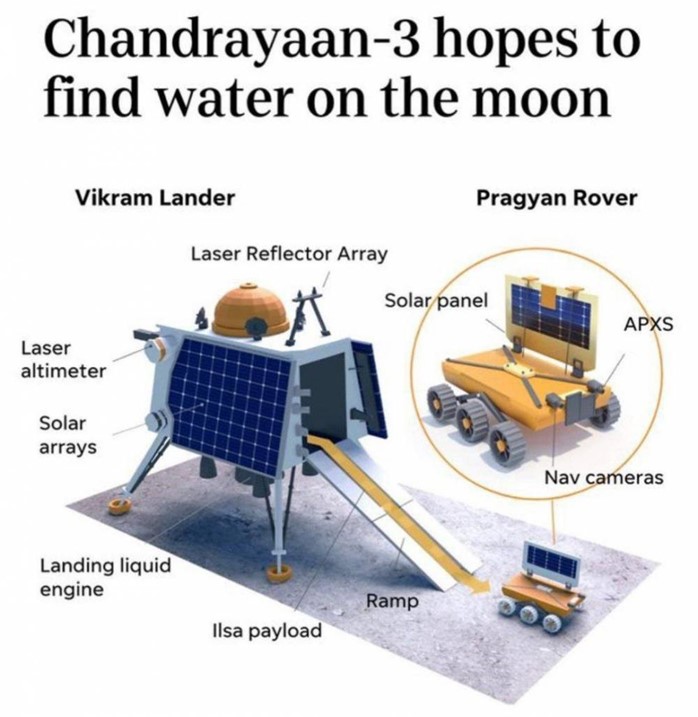
- Soft landing on the lunar surface near the lunar South Pole.This will make India the fourth country in the world to achieve a soft landing on the Moon.
- Deploy the rover, named "Pragyan," to explore the lunar surface and analyze its composition.
Scientific Objectives:
- Study the " Lunar topography", mineralogy, and elemental abundance
- Investigate the presence of water ice in the permanently shadowed regions of the Moon.
- Analyze the lunar exosphere.
- Study the composition and structure of the lunar crust and mantle.
Technological Objectives:
- Demonstrate the capability to perform a soft landing on the lunar surface, particularly near the challenging lunar South Pole region.
- Validate the performance of the indigenous rover and its scientific instruments.
- Enhance India's expertise in lunar exploration and related technologies.
C. Reasons for Chandrayaan-3 Landing near Lunar South Pole:
The decision to land Chandrayaan-3 near the lunar South Pole was motivated by several key scientific and strategic factors:
Scientific Reasons:
- Presence of Water Ice: The South Pole region is believed to hold significant deposits of water ice, potentially trapped in permanently shadowed craters.Studying this ice could provide crucial insights into the Moon's history, origin of water, and potential for future human exploration.
- Unique Geological Formations: The South Pole region exhibits unique geological formations, including ancient impact craters and volcanic features.These formations could reveal valuable information about the Moon's geological evolution and its early bombardment history.
- Unexplored Territory: The South Pole region remains relatively unexplored compared to other lunar regions.Landing there provides an opportunity to gather new data and make groundbreaking discoveries.
StrategicReasons:
- Technological Advancement: Soft landing in the challenging South Pole terrain would demonstrate India's advanced technological capabilities in space exploration and pave the way for future missions.
- International Recognition: Successfully landing a mission in the South Pole region would place India among a select group of nations with such accomplishments, enhancing its global standing in space exploration.
- Resource Potential: The presence of water ice and other potential resources in the South Pole region could play a vital role in future lunar exploration and development, making it a strategically important location.
FurtherConsiderations:
- Limited Sunlight: The South Pole region experiences extended periods of darkness.This poses challenges for solar-powered missions like Chandrayaan-3, requiring careful planning and energy management strategies.
- Harsh Environment: The South Pole region is exposed to extreme temperatures and radiation, necessitating robust engineering and design considerations for the lander and rover.
Overall, the decision to land Chandrayaan-3 near the lunar South Pole reflects India's ambition to explore the Moon' s most intriguing and scientifically valuable regions, while simultaneously advancing its technological capabilities and strategic position in space exploration.
D. Significance
I. Scientific Significance of Chandrayaan-3:
Chandrayaan-3, India's upcoming lunar mission, holds significant scientific value for various reasons:
1.Understanding Lunar Evolution:
- Studying the South Pole region, with its ancient craters and unique geological formations, can provide insights into the Moon's early history and its formation.
- Analyzing the composition of the lunar surface and exosphere in the South Pole region can shed light on the Moon's evolution over time.
2.Searching for Water Ice:
- The permanently shadowed craters near the South Pole are believed to harbor water ice deposits.Chandrayaan-3 will directly search for this ice using its scientific instruments, providing crucial information about the potential presence and distribution of water on the Moon.
- Understanding the abundance and distribution of water ice on the Moon is essential for future human exploration and resource utilization.
3.Studying Lunar Exosphere:
- Chandrayaan-3 will study the Moon' s thin exosphere, the outermost layer of its atmosphere.This will help understand the composition, origin, and escape of gases from the Moon.
- Exospheric studies can also provide insights into the interaction of the Moon with the solar wind and its influence on the lunar environment.
4.Advancing Technological Capabilities:
- Successfully soft-landing a mission near the lunar South Pole will demonstrate India's advanced technological prowess in space exploration.
- The mission will test and validate new technologies and instruments, paving the way for future, even more ambitious lunar and deep-space missions.
5.Contributing to International Lunar Exploration:
- Chandrayaan-3 will contribute valuable data and knowledge to the global scientific community, furthering our understanding of the Moon and its potential for future exploration and utilization.
- The mission will also strengthen India's position as a leading player in international lunar exploration collaborations.
II. Economic Significance of Chandrayaan-3:
While Chandrayaan-3 is primarily a scientific mission, it also carries significant economic implications for India in various ways:
1.Technological and Industrial Spin-offs:
- The development of advanced technologies for Chandrayaan-3, such as the high-precision lander and rover, will have spin-offs in various sectors like electronics, robotics, materials science, and telecommunications.
- This technological advancement can benefit various industries and contribute to economic growth.
2.Human Capital Development:
- Chandrayaan-3 has involved a large team of scientists, engineers, and technicians, contributing to the development of highly skilled human capital in the space and technology sectors.
- This skilled workforce can contribute to various high-tech industries and boost India's global competitiveness.
3.International Collaborations and Investments:
- Chandrayaan-3 has international collaborators, providing opportunities for joint research, technological exchange, and potential future commercial partnerships.
- Such international collaborations can attract foreign investments and boost India's space economy.
4.Public-PrivatePartnerships:
- Chandrayaan-3 has involved collaborations between government agencies and private companies, promoting the growth of the private space sector in India.
- Public-private partnerships can further stimulate innovation and economic growth in the space industry.
5.Educational and Public Outreach:
- Chandrayaan-3 inspires young minds to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields.
- Public outreach activities associated with the mission generate public interest in space exploration , potentially leading to increased government and private sector investments in space research and development.
6.Future Lunar Economy:
- The knowledge and experience gained from Chandrayaan-3 will be valuable for future lunar exploration missions, including potential resource utilization and commercial activities.
- India's early involvement in lunar exploration can help position itself as a key player in the future lunar economy.
III. Misc
1.National Prestige and Geopolitical Influence:
- The successful execution of Chandrayaan-3 would be a significant achievement for India, showcasing its growing technological prowess and ambition on the global stage.
- This accomplishment would enhance India's reputation as a leading spacefaring nation , bolstering its international standing and influence in global space exploration endeavors.
2.Inspiration for Future Generations:
- Chandrayaan-3 has the potential to inspire a new generation of scientists, engineers, and dreamers in India .
- The mission's success can ignite passion for STEM education and innovation, leading to a future workforce equipped to tackle the challenges of tomorrow.
3.Promoting International Cooperation:
- Chandrayaan-3 involves collaborations with international partners, fostering a spirit of cooperation and knowledge sharing in the global space community.
- This collaboration can lead to future joint ventures and contribute to the advancement of space exploration for the benefit of all humankind.
4.Exploring the Unknown:
- Chandrayaan-3 ventures into the relatively unexplored lunar South Pole, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and understanding.
- This spirit of exploration and discovery is fundamental to human progress and can inspire further scientific breakthroughs and technological advancements.
5.Laying the Foundation for Future Lunar Exploration:
- The knowledge and experience gained from Chandrayaan-3 will be invaluable for future lunar missions, including potential human exploration and resource utilization endeavors.
- By taking this bold step, India is positioning itself as a key player in the future of lunar exploration and development.
6.Symbol of Human Ingenuity and Collaboration:
- Chandrayaan-3 represents the culmination of human ingenuity, collaboration, and perseverance in the pursuit of knowledge and exploration.
- This mission serves as a testament to the boundless potential of human endeavor and inspires us to reach for the stars.
E. Chandrayaan-3 faces several significant challenges:
Technical Challenges:
- Soft Landing in Challenging Terrain: The lunar South Pole region presents a challenging landing environment due to its rugged terrain, craters, and slopes. Accurately navigating and achieving a safe touchdown will require precise control and robust engineering.
- Harsh Lunar Environment: The South Pole region experiences extreme temperatures, ranging from -173°C to 100°C. The mission must withstand these harsh conditions and maintain operational functionality for the planned mission duration.
- Limited Sunlight: The South Pole region receives less sunlight compared to other lunar areas. The mission must optimize its energy usage and rely on solar panels for power generation, considering the limited sunlight availability.
- Autonomous Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance: The rover needs to navigate autonomously in a complex and unknown lunar terrain. Advanced navigation algorithms and robust obstacle avoidance systems are essential for successful operation.
Scientific Challenges:
- Identifying and Accessing Water Ice: Locating and accessing potential water ice deposits within permanently shadowed craters requires specialized instruments and techniques. The mission must effectively identify and reach these deposits for scientific analysis.
- Analyzing Lunar Exosphere: Studying the Moon's thin exosphere presents challenges due to its low density and variability. The mission's instruments need to be highly sensitive and capable of capturing accurate data under these conditions.
- Interpreting Complex Geological Features: The South Pole region exhibits unique geological formations with complex histories. Analyzing and interpreting these features accurately requires expertise in lunar geology and data analysis.
Operational Challenges:
- Limited Communication Window: The distance from Earth and the lunar South Pole's location limit communication windows with the mission.Planning and executing operations within these limited windows is crucial for success.
- Mission Management Complexity: Coordinating the lander, rover, and scientific instruments from Earth requires complex ground station infrastructure, data management systems, and robust communication links.
- Contingency Planning for Unforeseen Events: The mission must have contingency plans to address potential technical failures, unexpected environmental conditions, or other unforeseen events that could impact mission objectives.

-1721391937657.png)

