EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES AND THREAT TO NATIONAL SECURITY
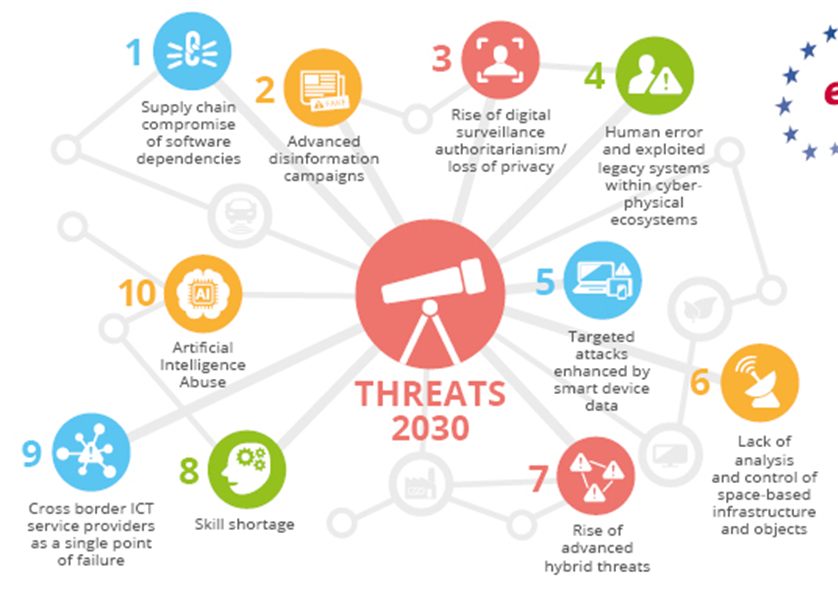
VARIOUS TECHNOLOGICAL TREATS TO NATIONAL SECURITY
CYBER SECURITY THREATS:
More Attack Surfaces: The connectivity of devices also lead sot more attack surfaces, with the increased in number new interconnected devices and Internet-of-Things (IoT) makes cyber threat environments bigger for potential attackers to expose deficiencies inside as well.
Advanced Cyber Threats: As the technology landscape continues to evolve, cyber threats are becoming increasingly advanced (using AI and ML).
Data Privacy Issues: New technology ecosystems often involve the collection and processing of large volumes of personally sensitive information (PSI), leading to concerns about data privacy, tendencies for misuse personal information.
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND GENETIC ENGINEERING
The Potential for Dual-Use: While scientific and technological advancements in biotechnology, such as gene editing or synthetic biology are holding great promise to solve global problems especially in medicine and agriculture, they can also be misused.
Bioweapons Development: Engineered pathogens could also be used to create biological weapons, which would present grave threats not only to public health but national security.
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): Genetic homo-virus- issues long terms of the impacts over health and environment need to consider with cautiously regulated.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) AND MACHINE LEARNING
Autonomous Weapons Systems: Attention to the development of autonomous weapons systems is echoed in the concern raised by artificial intelligence researchers about responsibility for decision-making by machines and side effects.
Algorithmic Bias/ Discrimination: AI algorithms can learn and propagate existing biases then discriminate certain groups of people.
Manipulation and misinformation: with the help of AI-ML, generated deepfakes so authentic that can deceive human senses to represent fabricated content as truth resulting in challenge on national security and social harmony.
QUANTUM COMPUTING:
Falling Encryption: Quantum computing has the hypothetical capacity to break our ebb and flow stages of encryption, undermining security for key communications innovation, business interests plus confidential data.
Cyber security Vulnerabilities: Quantum computing can help in finding a workaround for existing cyber security problems, but at the same time new dysfunctions will be created which have to be resolved.
SPACE TECHNOLOGIES:
Weapons in Space - i.e. that militarization earns threats to national security and could put vital ranges such as satellites at risk.
Space Debris: The growth of space debris jeopardizes the future sustainability of space operations and can have catastrophic consequences for those relying on satellite-based technologies.
MITIGATING THE THREATS:
Enhancement in Cyber security Defence - investments to be made towards a robust cyber security armory, having well-qualified professionals and threat intelligence will play a role of significant importance when responding to such adversarial operations.
International Cooperation: Global efforts must be made to tackle these new types of threats in regulatory, ethical guidelines as well as control mechanisms. Again,
Promoting Responsible Innovation: Emerging technologies can be fruitful but they must not lead to potential misuse and risk.
SECURITY CHALLENGES BY THE EMERGENCE OF TECHNOLOGIES
1. Larger Attack Surface- Every new device or computing technology deployed in the Estate of Things represents a potential hardware, software and network touch point for cybercrime.
2. Advanced Attacks: The attacks that hackers initiate are always getting more sophisticated, so organizations need to update their security systems frequently in order not been caught unprepared.
3. Concerns around Data Privacy: AI, and ML use a lot of personal data - this is bound to raise eyebrows with respect to the privacy issue.
4. Changing Regulations: Advances in data protection, AI, and other areas mean that the laws governing these applications are constantly changing.
5. Demand for cybersecurity professionals: The availability of expert and experienced staff remains a challenge in the face of an increased focus on security.
6. Greater dependence on technology: As society relies more upon its use, a cyberattack or natural disaster can cause unintended cascading side-effects.
7. Security Concerns in AI and ML: Adversarial attacks can alter the direction of output from an already-trained model, while biased data can be used to manipulate training processes so that outputs not only reinforce but also amplify socioeconomic discrimination.
8. Data Stored in the Cloud: When using cloud providers, questions around data security and privacy (among possible compliance issues) become very critical
9. Blockchain: Even though blockchain is designed for security, it may have vulnerabilities and weaknesses due to specific attacks such as Double Spending and Privacy Issues.
10. Technology is Constantly Changing: With the moving target of technology constantly present, security considerations are never static so they have to evolve in order to meet new threats.
BENEFITS OF TECHNOLOGIES IN NATIONAL SECURITY:
1. Advanced Situational Awareness: Advanced technologies like satellite imagery, radar and drones with live data help in collecting intelligence real time allowing the national defenc officials to have upgraded situational awareness.
2. Better Communication and Collaboration: Through secure platforms for communication as well as data-sharing mandates, the advantage of greater collaboration between different national security agencies contributing, ultimately to better operations.
3. Improved Cyber Security: The use of advanced capabilities like AI and ML can identify potential cyberattacks, thereby securing the methods by which national security systems or critical infrastructure are run.
4. Improved Targeting and Surveillance: Technologies ranging from precision-guided munitions to high-resolution imaging systems also more precisely target military action, in ways that should reduce collateral damage.
5. Force Protection and Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) with biometric identification systems such as facial recognition, advanced sensors including thermal cameras for mass fever screening and AI/ML analytics deliver better force protection IoT solutions.
6. Counterterrorism & Counterinsurgency: Identify and disrupt terrorist networks, counter insurgent activities w/ data analysis , social media monitoring, predictive algorithms
7. Humanitarian Disaster Response: Tools such as satellite communication, drones and analysis using Artificial Intelligence can help to provide efficient disaster response measures in case of adversity.
8. Border security and maritime domain awareness: Enhance capabilities of surveillance systems, drones with advanced sensors to adequately secure borders & prevent illegal activities including smuggling.
9. Intelligence Analysis & Prediction: AI, ML algorithms can analyse huge data to find patterns and predict future threats that will help take proactive national security measures.
10. First Responder Training and Simulation: New simulation technologies create more life-like training scenarios to prepare military personnel and first responders in advance of actual events, enabling them to know what they are supposed do before an event occurs.
ACTION TOOK BY GOVERNMENTS
1. FORMULATING NATIONAL CYBERSECURITY STRATEGIES
All governments are in the process of creating comprehensive national cybersecurity strategies, aimed at mitigating modern technology threats. These formulas mainly involves
Reinforcing critical infrastructure: Securing power grids, communication networks or financial systems against cyber attacks.
Improving cyber defence: Buy/develop new cybersecurity technologies and capabilities, as well as the necessary resources to detect intrusions before they happen.
Cybersecurity awareness campaign: To educate the public about cyber threats and to reinforce proactive best practices in cybersecurity.
Foreign-policy alliances: Foretoken and information sharing with other countries on cyber problems, collaboration in responding to attacks.
2. CREATE CYBERSECURITY AGENCIES AND LAWS
On the government side, many countries have focused these watchdog agencies that are responsible for governance and coordination of every national level efforts within cybersecurity in general.
Governments: Governments are responding by enacting new laws and regulations to address specific cyber threats such as data privacy regulation, cyber-crimes law or critical infrastructure protection standards.
3. INVEST IN RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT:
governments are investing massively on research & development against newly emerging technology threats.
The work centres on advancing cutting-edge cybersecurity technologies, helping prepare new programs in cyber defence intelligence and artificial intelligence for cybersecurity detection.
4. PRIVATE SECTOR PARTNERSHIP:
Governments are increasingly stepping up in collaboration with the private sector to exchange knowledge and create novel strategies to resolve cybersecurity threats.
5. FOSTERING INTERNATIONAL COLLABORATION
As many cyber threats are transnational, international cooperation is also essential to adequately respond them. They will only be able to strengthen their approaches by working together through international bodies .
they can share information and bring greater coordination on this issue), as well gemeinsame Standards nationally.
6. PUBLIC AWARENESS CAMPAIGNS:
Public awareness about cyber threats and tactics is a major priority to many governments who have launched public campaigns for safe internet practices.
These are about more general issues, like phishing scams and identity theft that may be related to good ole common sense practices
7.EDUCATION AND TRAINING:
Cybersecurity education and training programs are being funded by governments to produce a workforce skilled, educated and trained on how the ever changing cyber threats must be dealt with. Certifications for security professionals, people of authority and anyone else who uses them.
8.SUPPORTING INNOVATION:
Public sector innovation : Governments are funding new cybersecurity technologies, in order to encourage further research and development of innovative products or solutions.
9. CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTMENT:
Power grids, transportation systems and communication networks are being improved to become more resilient in times of cyber security attacks by governments.
10. DIPLOMATIC EFFORTS:
Governments are looking to diplomatic routes for addressing cybersecurity threats - including negotiating international agreements on norms of state behaviour in cyberspace.
MOVING FORWARD
1. Increased International Cooperation:
Support international cooperation and information exchange, R&D collaboration for cybersecurity enhancement, unified cyber responses.
Developing global norms for responsible behavior in cyberspace. Development of cybersecurity solutions through public private partnership.
2.Continuous Innovation:
Focusing On New Technologies Like AI and ML for Detection Capability .Stimulating innovation in the cybersecurity sector to create stronger and more efficient security approaches.
Promoting public-private partnerships for cybersecurity R&D and new technology development to fuel national pilot deployment efforts.
3.Holistic Cybersecurity Approach:
Taking a more comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that considers technical and nontechnical dimensions, human elements as well as organization-driven weaknesses.
Educating the public on cyber hygiene principles and encouraging good online habits Developing a skilled cybersecurity workforce through programs for education and training.
4.Building Public Trust:
Appropriate transparency and accountability around the use of surveillance powers, other cybersecurity techniques. Ensuring the security of all citizens while respecting individual privacy and civil liberties.
Communicate openly and candidly with the public about the nature of cybersecurity struggles, their own role in it
5.Continuous Adaptability:
Accepting that the technology landscape and adversaries are in a state of constant change, requiring ongoing evolution strategy and defence mechanisms. Enabling the right degree of agility and flexibility to respond appropriately when new threats or vulnerabilities are discovered.
Investing in resources necessary to enable long-term investments in national security research, infrastructure and workforce.
Only through focusing on these key areas and encouraging collaboration between government institutions, private industry, academia and the individual can an effective strategy to deal with changing technology pressures for national security segmented. By through continuing innovation, playing attack and work together ensures an all-over safety for the people as well is enables more stable nations in a world undergoing ever ongoing development within technology.

-1721391937657.png)

